What happens when you add location data to business data?
You complete the picture.
Geospatial analytics with tools like interactive, heat maps for example can let you visualise detailed geographic information, which when combined with data analytics, enable you to predict outcomes and uncover new market trends and patterns. Couple this with the Internet of Things (IoT) and Big Data, and organisations can collect any information about any location and event, in real-time.
Geospatial analytics basically involves the gathering and displaying of geographic information system (GIS) data to create models such as maps and graphs. Geospatial technologies are fast emerging in the world and are increasingly used by governments and business industries in the areas of urban planning, infrastructure development and disaster management among others. A GeoBuiz Report in 2018 states that the GIS/ Spatial Analytics in Asia Pacific is expected to grow at a CAGR of 18.2% during the period 2017-2020, and its market share is expected to increase from 29% in 2017 to 32.6% in 2020.1 Countries like Japan, Australia and Singapore are some of the advanced adopters of geospatial technologies.
Geospatial analytics is poised to open a world of possibilities and will play a pivotal role in helping industries innovate, develop new business models and stay ahead of competition. Elixir Technology’s GIS map engine is a tool that will support the industries’ innovation and growth. With Elixir’s GIS map engine for data visualisation, organisations can delve deeper into the data to reveal hidden geographic correlation and important insights along the way.
And in urban planning, Elixir’s GIS map engine can help to visualise and uncover correlations in data to better analyse citizens’ behaviours and patterns; thereby facilitating improvements to urban mobility and infrastructure planning among others.
Smart Urban Mobility
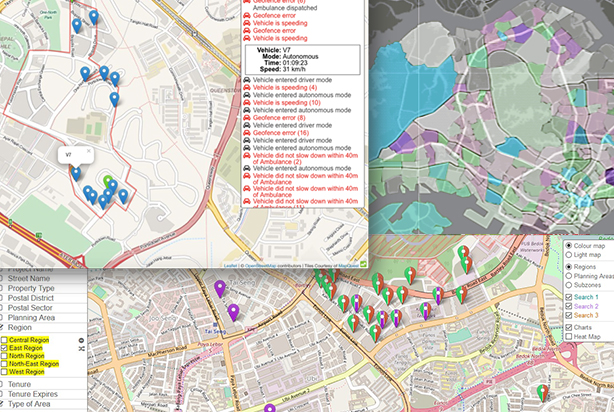
Smart urban mobility is about designing mobility solutions that takes into consideration, real-time traffic movements of commuters and modes of transport. Geospatial analytics can be integrated with data and video analytics, to visualise and analyse mobility patterns, made by commuters and various transport modes, for the planning of smoother traffic during peak hours.
Smart Infrastructure, Land and Road Planning
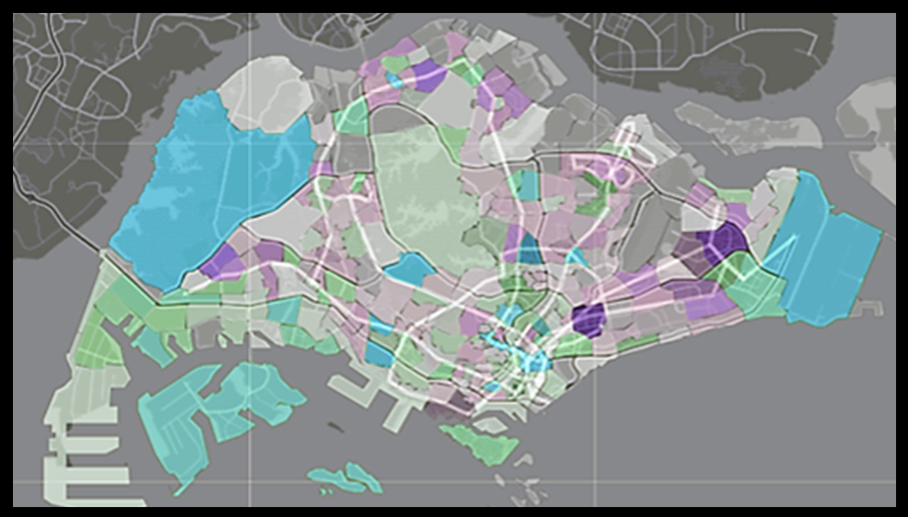
Social and Community Planning
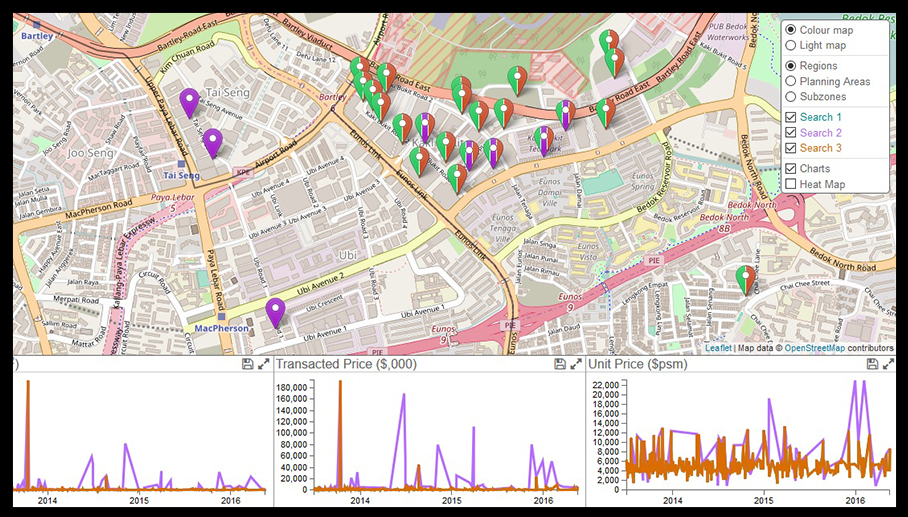
In the gathering of spatial and business data, urban planners can help to address pressing social and community issues; and thereby devise policies and initiatives to mitigate or resolve them. These wide-ranging issues may range from social integration of non-citizen members of the public to racial harmony among others.
Beyond urban planning, the geospatial analytics market is poised to grow across all industry verticals, led in part to an increase in non-spatial and spatial data, made available from the emergence and growth of ICT and disruptor technologies. Geospatial analytics will play a critical role in transforming governments and businesses through generation of new insights, development of innovative business models and frameworks, as well as uncovering of upcoming trends.
1 GeoBuiz Report 2018